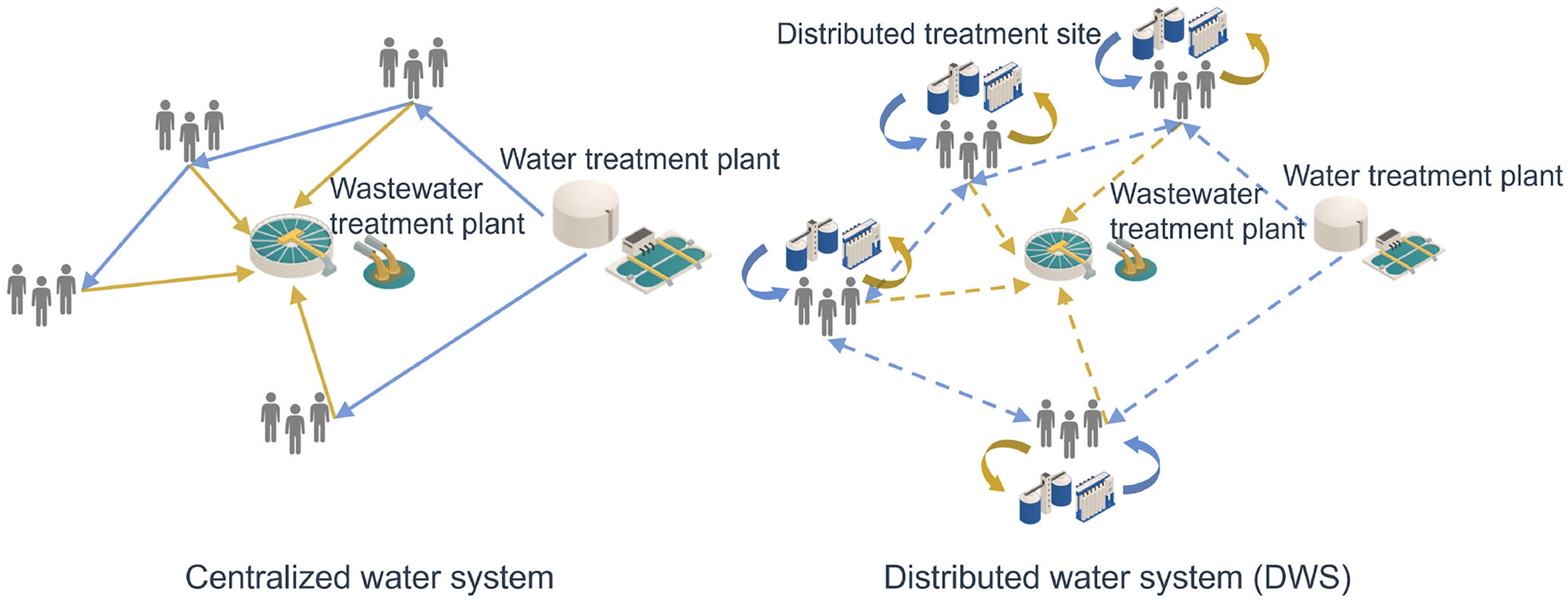
It is widely acknowledged that distributed water systems (DWSs), which integrate distributed water supply and treatment with existing centralized infrastructure, can mitigate challenges to water security from extreme events, climate change, and aged infrastructure. However, it is unclear which are beneficial DWS configurations, i.e., where and at what scale to implement distributed water supply. We develop a mesoscale representation model that approximates DWSs with reduced backbone networks to enable efficient system emulation while preserving key physical realism. Moreover, system emulation allows us to build a multiobjective optimization model for computational policy search that addresses energy utilization and economic impacts. We demonstrate our models on a hypothetical DWS with distributed direct potable reuse (DPR) based on the City of Houston’s water and wastewater infrastructure. The backbone DWS with greater than link and node reductions achieves satisfactory approximation of global flows and water pressures, to enable configuration optimization analysis. Results from the optimization model reveal case-specific as well as general opportunities, constraints, and their interactions for DPR allocation. Implementing DPR can be beneficial in areas with high energy intensities of water distribution, considerable local water demands, and commensurate wastewater reuse capacities. The mesoscale modeling approach and the multiobjective optimization model developed in this study can serve as practical decision-support tools for stakeholders to search for alternative DWS options in urban settings.
Mesoscale Modeling of Distributed Water Systems Enables Policy Search